However, safety concerns, especially regarding hepatotoxicity, have driven multiple trials, which have demonstrated the low incidence of statin-related hepatic adverse effects. The most commonly reported hepatic adverse effect is the phenomenon known as transaminitis, in which liver enzyme levels are elevated in the absence of proven hepatotoxicity.
"Ttransaminitis" is usually asymptomatic, reversible, and dose-related.
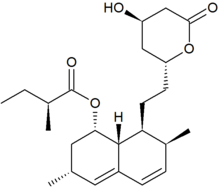
Lovastatin, a compound isolated from Aspergillus terreus, was the first statin to be marketed for lowering cholesterol. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
The increasing incidence of chronic liver diseases, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatitis C, has created a new challenge when initiating statin treatment. These diseases result in abnormally high liver biochemistry values, discouraging statin use.
A PubMed/MEDLINE search of the literature (1994-2008) was performed for this Mayo Clinic Proceedings review. The review supports the use of statin treatment in patients with high cardiovascular risk whose elevated aminotransferase levels have no clinical relevance or are attributable to known stable chronic liver conditions.
References:
Statins in the Treatment of Dyslipidemia in the Presence of Elevated Liver Aminotransferase Levels: A Therapeutic Dilemma. Rossana M. Calderon, MD, Luigi X. Cubeddu, MD, Ronald B. Goldberg, MD and Eugene R. Schiff, MD. Mayo Clinic Proceedings April 2010 vol. 85 no. 4 349-356.